Do You Pay Tax on an Inheritance? What’s the tax treatment of an inheritance? Depending on what type of asset you inherit, it could be considered taxable income. Funds from inherited retirement accounts are usually included in your taxable income. Taxes on cash, stock, or property inheritances are different, if tax applies at all. Whether you pay tax on an inheritance depends on what type of asset you inherit and how it was inherited.
How are inherited retirement accounts taxed?
Unlike inheritances of property or cash, when you inherit a retirement account like an IRA or 401(k), you typically must include funds in your taxable income when you take money out. If you inherit a retirement account from a spouse, you can treat the account as your own. If the account was inherited from a parent or non-spouse, you have 10 years to take the money in most cases. RMDs may also apply.
If you inherit a Roth IRA, earnings are generally tax-free as long as a 5-year holding period has been met. Initial contributions to a Roth IRA are tax and penalty-free.
Under the Secure Act, which was passed in 2019, beneficiaries who inherit a retirement account from a non-spouse (e.g. a parent or relative) can no longer ‘stretch’ the distributions over their lifetime by taking required minimum distributions (RMDs).
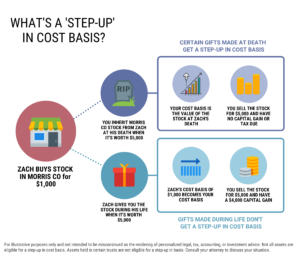
Do you pay tax on inherited stock?
If you inherit a taxable investment account (also called a brokerage account) or assets that were in a revocable trust at the decedent’s death, you may have limited federal capital gains tax exposure when you sell the position.
At a high level, here’s how this works:
When you buy stock, the cost basis for tax purposes is your purchase price. Later, when you sell the stock in a taxable account, you calculate your gain (or loss) by how much you sell the position for (the market value). The tax rate will depend on how long you owned the stock for.
But when stocks are inherited, the heir can apply to receive a step-up in basis to the market value of the security at the time of death. (An alternate valuation date could be elected but it’s less common). In this example, when you sell the stock, you pay capital gains taxes on the difference between the stepped-up cost basis and the sale price. Stepped-up basis are always considered long-term regardless of the actual holding period.
This is one reason why a brokerage account can be a good way to leave a legacy. The same tax treatment can apply to inherited property like a home or rental property.
If you sell at a loss, you can offset other investment gains plus an additional $3,000. When the loss is greater, you can carry it forward to future tax years. If you inherit securities, the holding period is always long-term for tax purposes.
Very important notes and caveats
Note #1: The above description generally applies to assets that pass through the decedent’s taxable estate. If you are inheriting money in a trust other than a revocable trust, the tax treatment may well differ. This includes whether the assets are eligible for a step-up in basis, the tax rates, who is responsible for paying the tax and even has control of the assets/distributions. Speak with your attorney and tax advisor to discuss your situation.
Note #2: federal and state estate tax implications are different and may still apply, both of which can impact the remaining liquidity and assets available for beneficiaries. This discussion is outside the scope of this article. Discuss your situation with the trust and estate attorney for the estate.
Inheriting a Trust Fund: Distributions to Beneficiaries
Federal and state inheritance tax
There is no federal inheritance tax for cash or property. However, some states have an inheritance tax. Iowa, Kentucky, Nebraska, Pennsylvania do have an inheritance tax which the beneficiary may be responsible for. Two states: New Jersey and Maryland have both an estate tax and an inheritance tax. There are exemption amounts which vary by state. Whether a tax is due may also depend on your relation to the decedent. Ask your tax advisor whether this may apply to your situation.
Are life insurance proceeds taxable income?
As the beneficiary, you likely will not owe income tax on the death benefit from a life insurance policy. If you take life insurance proceeds in a lump sum, you won’t have to pay income tax. However, if you take the funds in installments, the interest is taxable.
Although installment payments can help less confident investors by providing an “allowance” for the proceeds, also consider working with an independent fee-only financial advisor to develop an investment management strategy that’s tailored to meet your personal goals and maximize your wealth.
Help managing sudden wealth from an inheritance
If you are about to receive an inheritance, you likely have some questions about the process and if you will need to pay tax on your inheritance. Darrow Wealth Management is a fee-only wealth management firm in Boston and Needham, MA. We specialize in helping individuals plan and invest after a sudden wealth event. Schedule a free consultation to learn more about how a comprehensive financial plan can help make the most of your inheritance.
Darrow Wealth Management does not provide tax and/or legal advice. Certain circumstances may require us to coordinate with your qualified tax and/or legal advisor.
Last reviewed April 2024